As in the past weeks, the Grusch Affair continues to send out ripples and froth that obscure the more profound depths of the phenomenon.
Ballester-Olmos, et al, published their relatively down-to-earth review of the recent U.S. National Security Subcommittee’s hearing on UAP:
We don’t know whether to label it as ridiculous or shameful. Under the guise of a bipartisan initiative, the real scenario is a group of mostly Republican politicians seemingly trying to undermine the Democrat administration, using the tenuous pretext of UFOs this time around.Whether they are naive, misinformed, driven by ideology, or simply gullible remains unclear
Nevertheless, the appetite for the matter unsated, The Hill has organized a panel, We Are Not Alone: UFOs & National Security for 17 August 2023, with three of those “Republican politicians” and, finally, someone who knows something, historian Greg Eghigian. The Hill‘s own Marik Von Rennenkampff and Baptiste Friscourt at UAP Check have both recently published articles, more interesting for their logic than their content….
The most turbulent development was the paranoid reaction to The Intercept‘s revealing Grusch’s history of PTSD and related mental health issues, Grusch’s defenders impugning that his records had been leaked as part of a smear campaign (they weren’t: “The records were not confidential, medical, nor leaked. They are publicly available law enforcement records obtained under a routine Virginia FOIA request to the Loudoun County Sheriff’s Office and provided by the office’s FOIA coordinator”). Logically, Grusch’s mental health history can hardly be said to discredit his testimony (that would be a very weak ad hominem argument), no more than his being autistic. More concerning is his business affiliation with Gary Nolan’s Sol Foundation, whose director is Chris Mellon, which associates Grusch all the more glaringly with those most prominent in promoting the UFO (rebranded as UAP) mythology post-2017….
Friscourt in his article for UAP Check invokes a common, ufological / astrobiological argument: “Statistical studies show that we can’t be alone;” if we have launched space probes, “others probably did it, as we are statistically unlikely to be special;” “Once you consider the amount of possible life out there, extended over billions of years, statistics make it simple: the existence of [extraterrestrial spaceships piloted by] non-human bodies actually makes sense.”
I have posed here the question as to whether an argument for life on other planets, let alone so-called intelligent life, let alone “technological” life, can be made on purely statistical, probabilistic, mathematical grounds. And it is a question. The further the argument moves from the question of mere life on other planets, it seems to me less compelling. And even if such an argument can be validly made, it can still be asked if it isn’t oriented, guided, or otherwise “determined” by ideology (an unconscious affirmation of the universal naturalness of the social formation of the so-called “advanced” (capitalist) societies) or what I have called “a metaphysical residue,” an inherited idea of “essence” or Eternal Recurrence.
Ideas don’t fall from heaven. At birth, a human being is “thrown” into a time and place not of their choosing, one wherein they take up mostly unconsciously what German philosopher Hans-Georg Gadamer has called “Tradition”. Human beings’ being historical in this radical sense explains how it is certain notions orient, guide, and otherwise determine their actions, perceptions, and thinking. This “throwness” helps explain, further, in one regard, how ufological and astrobiological thinking can be seen to be guided by distantly-inherited ideas, such as a dim echo of Plato’s Forms.
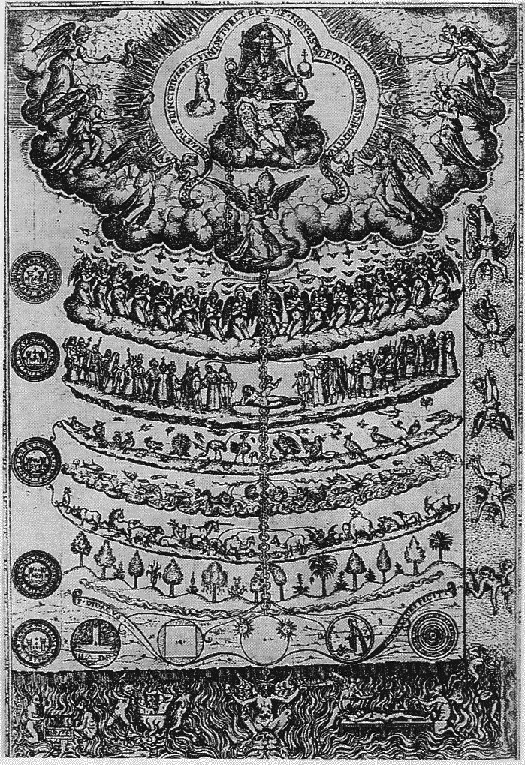
A recent Big Think article by Prosanta Chakrabarty suggests another such guiding idea: the Great Chain of Being, “still how many people understand (or rather misunderstand) evolution — that is, as a linear process with bacteria and plants at the bottom as ‘primitive’ and a straight line from fish → amphibians → reptiles → mammals and then humans as a distinct category at the top.” The fetishization of instrumental rationality (what is seen as giving us “technology”) let alone human intelligence is a case in point: it surely sets (technoscientific) human intelligence above all others. Moreover, the linearity of the Great Chain harmonizes with the “Platonic” idea that intelligence is measurable on such a linear scale, such that we can imagine aliens or A.I.s “more” intelligent than present-day Homo Sapiens (a linearity that gets in turn extended to technological sophistication, equally supporting, e.g., Maitreya Raël’s fancies about his alien teachers’ being “25,000 years ahead of us,” European explorers’ belief in their superiority to the indigenous peoples of Turtle Island, or even the Kardashev Scale).
That ufological or astrobiological thinking might well be said to be possessed by this scheme is an index of its being ontotheological, an inescapable consequence of its arising within the horizon of modernity, one in the grip of the Platonic-Christian inheritance, that fateful confluence of Greek ontology and Christian theology. It’s only once this “ufological / astrobiological unconscious” is revealed that that grip might begin to be loosened. Perhaps the nascent science of UAP studies (let alone the ufologically-minded) needs undergo a kind of conceptual psychoanalysis to free it from this perverse narrowness of vision before it is mature enough to join the family of full-fledged sciences.